May 27, 2025
A solar system isn’t just about installing panels—it’s about precision. You can have the best equipment, but if your layout design isn’t right, you’re leaving energy (and money) on the table.
Many homeowners and installers realize too late that their panels weren’t optimized for sunlight, shade, or tilt.
If you're planning or managing a solar project, whether residential, agricultural, or commercial, this guide is for you.
In this guide, we’ll break down how a well-planned solar panel layout can make all the difference between “just another installation” and a truly efficient energy system.
The Right Panel Layout for Solar Design: How to Maximize Efficiency
Switching to solar is more than a trend; it's a meaningful decision for your future, your wallet, and the planet.
"But when installed, it is sometimes, why isn’t my solar system performing like I expected?"
Many homeowners, farmers, and even solar installers ask this question after investing in a solar power system.
Surprisingly, the answer is often simple: the layout design was never optimized properly in the first place.
Yes, that rectangle of panels on your roof or field might look fine, but is it generating the maximum possible electricity? Is the solar irradiance fully utilized? Did your designer account for shading, angle, storage, and load needs?
Key Takeaways
- The design and placement of solar panels directly affect how much power your system generates.
- Roof vs. ground mount layouts each have unique advantages depending on location and project size.
- Factors like tilt angle, azimuth, shading, and airflow play a crucial role in optimizing efficiency.
- Smart design platforms like Sunbase simplify the process—offering real-time data, shading analysis, ROI modeling, and permit-ready documentation.
- A well-optimized layout ensures maximum energy yield, faster payback, and long-term system stability.
The Basics: What Makes Solar Design Layout So Important?
Imagine trying to grow crops without checking where the sunlight hits your land. That’s how some solar panels are installed, without a real solar design layout.
A layout is more than panel placement. It’s the blueprint that determines how much energy your system can produce, how stable your operation will be, and how soon you’ll see a return on your investment.
A good layout involves:
- Panel orientation and tilt
- Shading analysis using satellite imagery and LIDAR
- Solar irradiance mapping
- DC to AC conversion planning
- System sizing and inverter placement
- Roof or ground-mount suitability
- Battery and storage design
- Financial analysis and utility savings forecasting
It brings together all project requirements, equipment choices, and installation considerations into a unified, high-performing system.
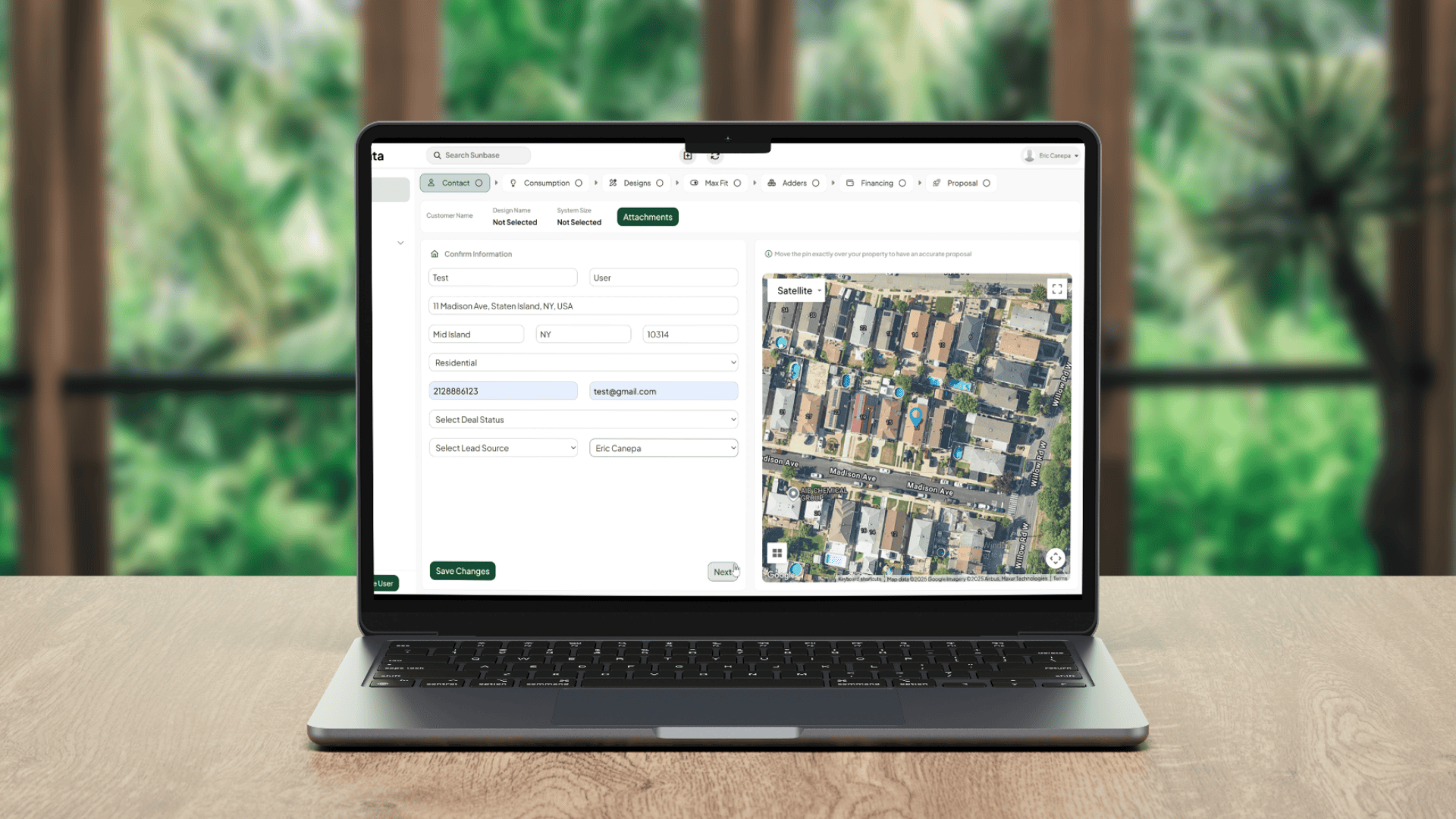
With advanced platforms like Sunbase, solar installers can create designs that consider all the critical factors using real-time satellite imagery, irradiance data, and building measurements. The result? Smart layouts, better outcomes.
Take a look at: Top Challenges for Solar Installers and Solutions to Overcome
Know Your Space: Roof vs. Ground Mount
Before you install a single panel, you must identify where the system will perform best.
1. Rooftop Solar Systems
Roof Mount is ideal for:
- Residential homes
- Small-to-medium businesses
- Locations with limited open land
Factors that affect rooftop installations:
- Roof areas (size, shape, slope)
- Orientation and pitch
- Shading from nearby trees or buildings
- Local construction materials and permits
Rooftop systems are convenient but require careful shading analysis to avoid significant output losses.
2. Ground-Mount Solar
In open areas, farms, or for large-scale commercial use, ground-mount systems offer flexibility and better positioning:
- Easier optimization of tilt and azimuth
- More space for airflow between rows (which enhances panel performance)
- Suitable for agriculture-integrated solar (agrovoltaics)
Ground-mounted panels often have higher energy production potential due to custom layout possibilities and reduced shading. While ground-mounted systems offer flexibility and optimal sun exposure, they require additional permits, mounting structures, and more land area.
3. Solar Irradiance and Shading: Reading the Sunlight Map
Every inch of sunlight matters when trying to convert sunlight into electricity. Not all sunlight is created equal.
The amount of solar energy your site receives, known as solar irradiance, can vary depending on your location, season, and time of day.
Shading, even partial, can drastically impact your system’s performance. A single shaded panel can bring down
the output of an entire string. That’s why a shading analysis is essential.
Use tools like:
- Satellite imagery
- LIDAR scans
- Weather databases
- Real-time solar design software
This data helps calculate irradiance, identify low-performing areas, and design a system with maximum exposure.
Pro Tip: Many underperforming systems suffer due to missing this step. Even partial shade can drop a panel’s output by over 30%!
The Right Layout: Panel Placement for Peak Efficiency
Think of solar panels like sunbathers on a beach; they need just the right angle, space, and positioning to soak in the sunlight efficiently.
But this isn’t just about exposure; it’s about engineering a layout that works in harmony with your location, property type, and energy goals.
Whether it's a rooftop installation or a ground-mounted system, a well-thought-out layout can significantly impact your overall energy production and return on investment.
Here’s what goes into optimizing your solar panel layout for peak efficiency:
1. Azimuth: The Compass Direction That Guides Your Panels
Azimuth refers to the compass direction your panels face. In the Northern Hemisphere, a true south-facing orientation is generally ideal because it receives the most direct sunlight throughout the day. However, this can vary based on:
- Roof orientation: If your roof faces east-west, installers may split the system across both sides.
- Energy usage patterns: If your energy use peaks in the afternoon, a slightly west-facing azimuth might yield better real-world savings.
- Shading: Even a perfectly south-facing roof may underperform if nearby trees or structures partially shade it.
2. Tilt Angle: Aligning with the Sun's Path
The tilt angle is the angle between the panel and the horizontal surface. Getting this right ensures your panels are perpendicular to the sun’s rays for most of the day, which maximizes energy absorption.
- Rule of thumb: The ideal tilt angle is typically equal to your geographic latitude. For example, if you live at 30°, a 30° tilt is a great starting point.
- Seasonal adjustments: Some systems in snowy or variable climates use adjustable tilts, steeper in winter to shed snow, flatter in summer to capture high sun.
- Flat roofs: Tilted mounting racks are used to create the ideal angle and avoid water pooling.
3. Row Spacing in Ground-Mounted Systems: Preventing Self-Shading
For ground-mounted solar systems, layout isn’t limited by roof shape, so you get more control. But spacing between panel rows is crucial.
- Why spacing matters: As the sun moves across the sky, one row of panels can cast a shadow on the row behind it, especially in winter when the sun is lower.
- Design tip: A general guideline is to leave enough space so the front row doesn’t shade the one behind it during peak sunlight hours. The right tools can calculate the optimal row spacing based on your coordinates and system height.
4. Airflow: The Hidden Factor That Affects Panel Performance
Most people don’t realize that solar panels lose efficiency as they heat up. That’s why airflow is a critical but often overlooked factor in solar design.
- Cooling effect: Elevating panels slightly from the roof or ground allows air to circulate beneath them, naturally cooling the system.
- Performance gain: Proper airflow can improve efficiency by up to 10% in hot climates.
Simply put: It's Not Just About Placement, It's About Performance
Optimizing layout means more than just “fitting panels where they go.” It’s about making informed decisions using design tools, solar irradiance data, and physical site conditions to maximize production, avoid energy losses, and prolong system life.
With tools like Sunbase, you can simulate multiple layout options using real-world data, factoring in azimuth, tilt, row spacing, and shading, to find the setup that delivers the most consistent electricity during peak sun hours.
Also read: Best Solar Design Software for Accurate Layouts
Sizing, Storage, and Inverters: Matching System Capacity to Real Needs
Oversizing your system doesn’t guarantee better performance, and undersizing leads to missed opportunities.
Every property has different energy demands. A solar system should be sized based on:
- Monthly electricity usage
- Utility costs
- Future needs (like EVs or home expansions)
Understanding:
- System capacity (measured in kilowatts)
- How much DC electricity will your panels produce
- How does that convert to usable AC electricity for your home or business
Battery storage adds resilience, especially for areas with grid instability. The right battery size depends on your goals: backup power, self-consumption, or full off-grid use.
Quality of equipment matters, too. Good panels, reliable inverters, and well-integrated storage systems ensure performance and longevity.
Using a solar design software platform like Sunbase, you can input your location, structure type, and load profile to calculate the perfect system size and test designs, as well as simulate your savings before the first panel is even delivered.
Financial Analysis: Beyond Installation Costs
Many people ask, "How much do solar panels cost?" But the real question should be:
"How much can I save and earn through this system over time?"
Before installation begins, there's planning to be done.
Cost Considerations:
- Panels
- Inverter
- Mounting hardware
- Labor and installation
- Battery storage (if any)
With the right financial analysis, you can:
- Understand your ROI and payback period
- Factor in government incentives, rebates, and net metering policies
- Include operational costs, maintenance, and replacement timelines
- Make data-driven decisions on equipment choices
Incentives like solar tax credits, net metering, or local subsidies can reduce your solar cost significantly. Always check your eligibility before starting the project. Sunbase’s calculator can model various layouts and components to give you real-world cost-benefit insights based on your specific location and utility provider.
Permits, Inspections, and Project Readiness
Every solar installation, big or small, must align with local regulations.
This includes:
- Necessary permits
- Utility interconnection agreements
- Structural assessments
- Fire code compliance
- Inspection timelines
Tracking documentation can be overwhelming for large or multi-site projects. Software solutions and project management tools can streamline your approval process and keep timelines on track.
Performance and Monitoring: Staying Efficient After Installation
Once installed, your system must be able to track data and report problems.
Good solar systems include:
- Monitoring software
- Performance dashboards that track energy production
- Alerts for shading or equipment faults
- Historical comparisons for seasonal changes
- Compatibility with smart apps or phone integrations
Continuous monitoring helps enhance performance, extend system life, and boost your savings, especially when weather or usage fluctuates.
How Sunbase Helps: Tools that Simplify Design and Improve Outcomes

Sunbase is more than just solar design software; it’s your intelligent co-pilot for navigating every phase of a solar power project, from site evaluation to system installation.
Whether you're a solar installer, a homeowner planning a rooftop system, or a business exploring large-scale ground-mount installations, Sunbase equips you with the tools to make better, faster, and more confident decisions.
Here’s how it transforms complex solar design into a streamlined, insight-driven process:
1. Advanced Shading Analysis for Accurate Energy Predictions
- Sunbase uses satellite imagery, LIDAR data, and smart AI tools to analyze shading in just a few clicks.
- Instantly identify nearby obstacles, trees, chimneys, utility poles, or neighboring buildings that may cast shadows on your panels.
- Predict solar irradiance throughout the year and across different seasons.
- Optimize placement to avoid shaded zones and improve power output and long-term system performance.
2. Precision Layout Planning Using Aerial and 3D Mapping
With Sunbase, you can design the most efficient solar panel layout directly on your site's satellite or drone imagery.
- Easily map roof areas or open land with drag-and-drop tools.
- Set the optimal tilt angle, azimuth, and row spacing based on your site’s sunlight exposure.
- Test different configurations for roof-mounted or ground-mounted systems.
- The software ensures every panel is placed for maximum exposure while complying with structural and local code requirements.
3. Financial Analysis and ROI Modeling Made Easy
- Sunbase brings financial clarity to your solar decisions.
- Generate a detailed cost breakdown of the entire solar installation, including panels, inverter, labor, equipment, and battery storage.
- Run custom ROI calculations based on your location’s utility rates, energy consumption patterns, and incentives like solar tax credits and net metering.
- Quickly compare multiple design options to determine which layout offers the best payback period and long-term savings.
4. Permit-Ready Documentation to Accelerate Approval
- One of the biggest bottlenecks in any solar project is paperwork. Sunbase simplifies this too.
- Automatically generates permit-ready documents that comply with local regulations.
- Includes accurate system sizing, component specs (like inverter, battery, etc.), and layout visuals for smoother grid approval.
- Reduces back-and-forth with local authorities, saving you time, cost, and frustration during the installation phase.
5. Designed for Everyone, From Homeowners to Solar Experts
- Homeowners can visualize how many panels their roof can support, estimate electricity savings, and understand key factors like shading and storage needs.
- Installers and designers use Sunbase to optimize designs, impress clients with professional proposals, and minimize manual errors.
- Businesses and agricultural sites can explore ground-mount systems at scale, considering load demands, shading patterns, and energy needs.
Sunbase bridges the gap between technical expertise and everyday usability, making high-performance solar systems more accessible, efficient, and aligned with your unique project requirements.
By combining accurate layout planning, energy forecasting, and financial modeling in one intuitive platform, Sunbase empowers you to confidently and intelligently manage your solar investment.
Conclusion
Designing a solar power system is like tailoring a suit: It must perfectly fit your energy needs, space, lifestyle, and budget.
From form to function, from bill reduction to grid independence, solar success starts with smart layout planning, accurate calculations, and the right tools.
Whether you’re a solar company, an installer, or a homeowner who wants to be well-informed before signing a contract, understanding solar design can mean the difference between an average system and a truly efficient, high-performance energy generator.
About Sunbase
Sunbase is more than just a layout tool. It combines everything, from sunlight data and shading analysis to financial modeling. Users find it helpful not just for designing smarter, but for presenting clear and reliable plans to clients, inspectors, and financiers.
Ready to see how your roof or land could generate clean energy? Start by booking your demo with Sunbase.
FAQ's
How accurate is Sunbase’s shading analysis compared to manual surveys?
It uses satellite imagery and LIDAR data to deliver highly accurate shading analysis, often matching or exceeding manual site visits.
Can Sunbase help choose between rooftop and ground-mounted systems?
Yes, it compares both options based on space, orientation, and cost, helping you make the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
How do I know if I’m placing too many or too few panels on my roof?
The number of panels should match your energy needs, roof space, and utility rates; a layout tool uses these factors to calculate the right capacity.
I agree to receive marketing messaging from Sunbase at the phone number provided above. I understand data rates will apply, and can reply STOP to OPT OUT.